Radiographic examinations
Oral inspection alone is often not sufficient to establish an accurate diagnosis of a patient and to plan the most effective treatment. X-ray examinations allow dentists to see the entire bone anatomy of the jaw, find the roots and channels of individual teeth, and create a digital three-dimensional image of the mouth for high-quality modelling of prostheses. Radiological images of the patient’s teeth are used in the treatment of dental root canals, various surgical operations, orthodontic straightening, dental filling, and implantation. All the examinations performed in our clinic use modern equipment, which is completely safe, and the procedure takes only a few minutes.
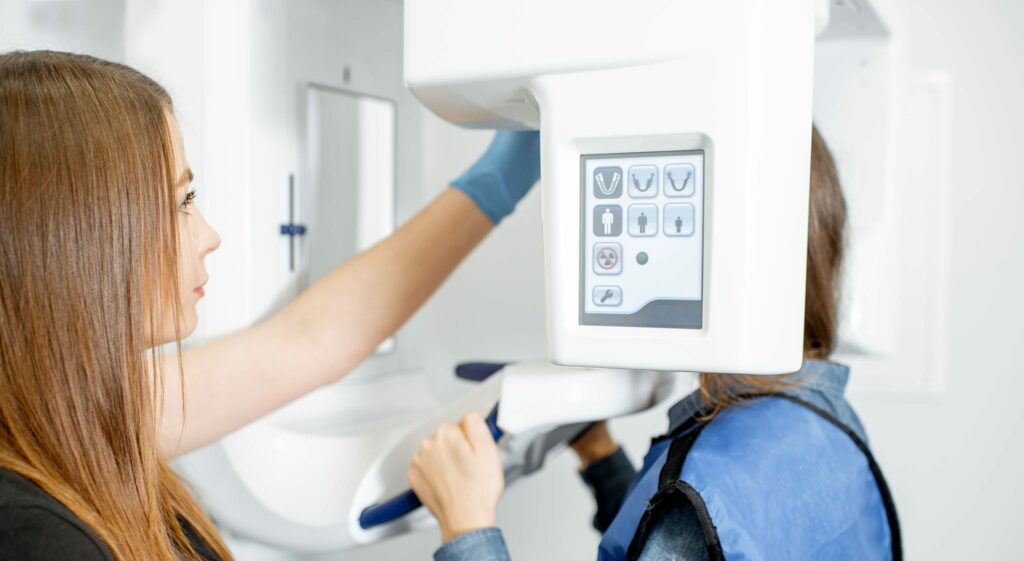
Panoramic dental X-ray
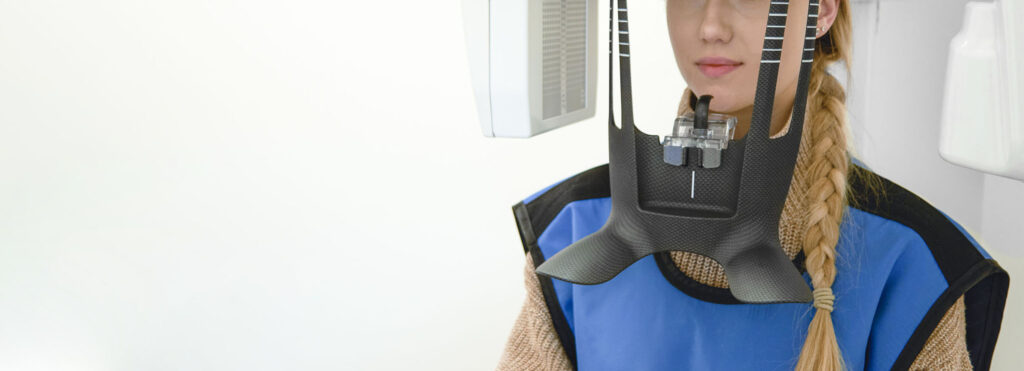
A panoramic X-ray shows all of a patient’s teeth, jaw joints, sinuses, and soft tissues. The photo is called panoramic since it captures a wide view of both jaws centred in a single horizontal line.
The panoramic X-ray is simple to perform: the patient stands up to a special X-ray machine called orthopantomograph, bites the plastic clamp with the front teeth to ensure stability and holds the hands behind the handles. The device creates an image of the jaw in just 20-30 seconds. The X-ray image can then be printed or a digital version of it used.
A panoramic photo may be required:
- Before implantation to assess the condition of bones and to select the most effective structure.
- Before orthodontic treatment to plan the orthodontic system’s structure. Also during the orthodontic treatment to record and examine the intermediate outcome of the treatment.
- Before oral surgery.
- To localise occult tooth decay, cysts, granulomas, and other oral neoplasms.
- Before a difficult tooth extraction, it is necessary to assess not only the condition of the tooth to be removed but also the condition of the surrounding tissues.
- To accurately determine the extent of periodontal lesions.
- To determine the position of impacted wisdom, or other, teeth.
- To control the formation of teeth and jaws in children.
Periapical X-ray

A periapical X-ray is an image of a specific area of the jaw that shows an accurate anatomy of the roots of individual teeth and their canals. It is used to evaluate the damage caused by tooth decay or other dental diseases, or physiological abnormalities of single teeth.
A visiograph is used to take periapical X-rays by emitting a small number of X-rays and transmitting the data to a computer, where it is converted into a digital image of the scanned area. The dose of radiation emitted by the visiograph is very low compared to a conventional X-ray machine, making a periapical X-ray a safe and harmless test.
A Periapical X-ray may be required before the treatment of the root canals. It allows the endodontist to find and shape the dental canals, performing the treatment with as little damage to the dental tissue as possible. A periapical image is also taken prior to prosthetics of a single tooth, or a few adjacent teeth, to accurately determine the distance to the jaw canal.
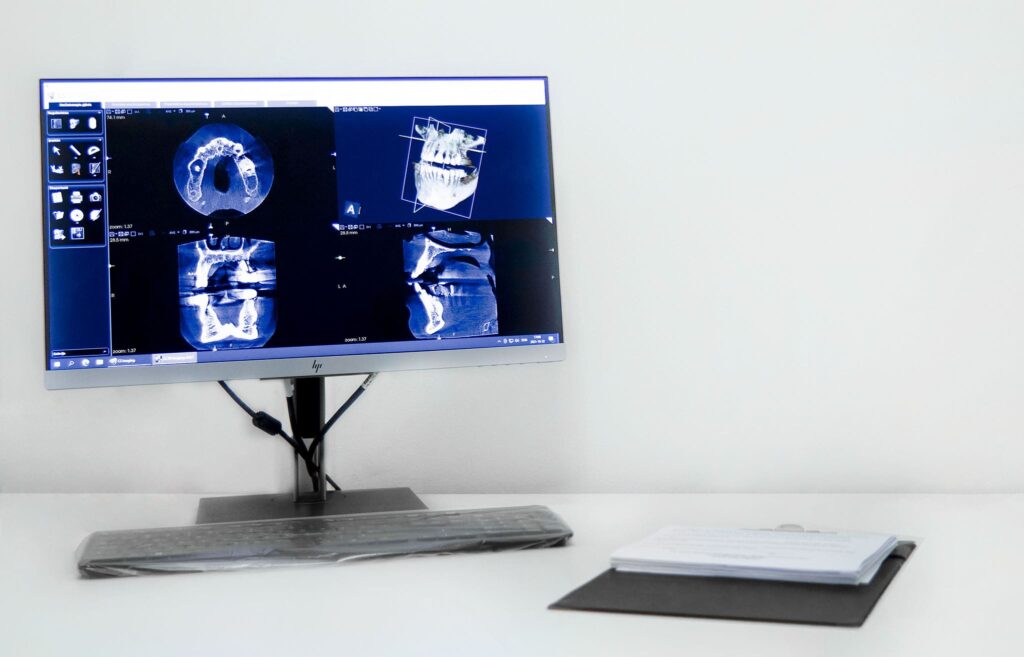
3D computed tomography
3D computed tomography (CT) allows us to not only to see a flat anterior view of the jaws, or even a specific tooth, but also to examine the teeth, gums, and entire oral anatomy of the mouth from all sides. CT provides a 3D model of the entire human oral area which allows for more effective treatment planning.
This procedure is performed with a 3D dental tomograph – a modern and accurate piece of equipment, the radiation dose of which is up to 10 times lower than that of standard spiral CT devices. 3D tomography produces the highest quality X-ray images, which is why 3D CT has gained great popularity in modern dental clinics.
3D CT is one of the most informative radiological examinations used:
- For implantation, to examine the anatomy of the dental bone and accurately determine the implantation site.
- For bone augmentation, when determining the shape and volume of bone in the jaw area required for implantation.
- For the treatment of teeth by localizing the root canals and detecting recurrent tooth decay, cysts, and other inflammations.
- For tooth extraction by determining the number of tooth roots and their locations in the jaw, minimising affected teeth.
- For orthodontic treatment by diagnosing occlusal defects and planning the most effective method of their treatment.
Pricelist
Radiographic examinations
| Panoramic dental X-ray | 55 € |
| Periapical X-ray | 20 € |
| 3D computed tomography | 120 € |
