
Anaesthesiological treatment
Different types of anaesthesia are offered not only to children but also to adults. This allows all patients to comfortably perform even the most difficult operations, get rid of the anxiety of dental procedures and fear of pain.
Types of anaesthesia
The goal of modern dental treatment is to not only cure the teeth, but to also ensure the patient’s comfort during the treatment. Anaesthesia allows us to get rid of unpleasant sensations when treating dental root canals, performing dental filling, periodontal and surgical operations, as well as other procedures.
Some people, especially children, are often afraid of dental procedures and cannot sit quietly in the dentist’s chair, feeling uncomfortable. In order to protect the child’s psycho-emotional state while allowing the dentist to restore the quality of the teeth, sedation and general anaesthesia are often suggested in children’s dental treatment.
Local anaesthesia
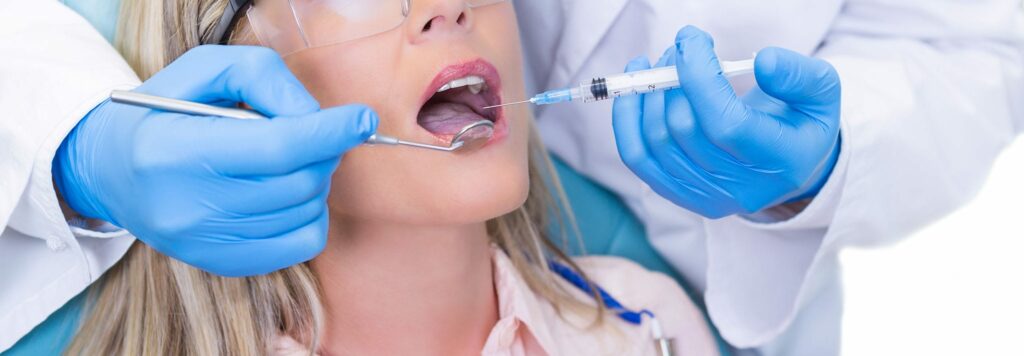
The simplest and most commonly used method of anaesthesia. For local anaesthesia, an injection is made into the soft tissues of the mouth which takes effect almost immediately and ensures complete numbness for the area of the mouth being treated. A very thin needle is used to inject the local anaesthetic, making it almost painless.
This method of anaesthesia is used for dental fillings, installing orthodontic implants, during simple oral surgeries, and other short-term and non-interventional dental procedures.
Local anaesthesia is the best method of relieving pain during simple dental procedures as it allows us to get rid of unpleasant sensations without suppressing the patient’s general nervous system.
Sedation

Special medications used during sedation help the patient to reach a light sleep state. The patient remains conscious, but completely relaxes, does not pay attention to the surrounding environment, and does not feel fear. The patient does not retain any unpleasant memories of a procedure performed with sedation. Therefore, this method of treatment makes it easier for children to get used to oral treatment.
Sedation does not prevent pain. During sedation, the patient can still feel all the actions of the dentist, but due to the relaxation of the muscles and nerves, they do not quickly react to them. Therefore, sedation may be combined with local anaesthesia during potentially painful procedures.
This method of anaesthesia is most commonly used in children and adults who are anxious about dental treatment. Sedation provides an opportunity to treat hyperactive children as well as patients with uncontrolled physiological actions (e.g., increased nausea reflex).
General anaesthesia
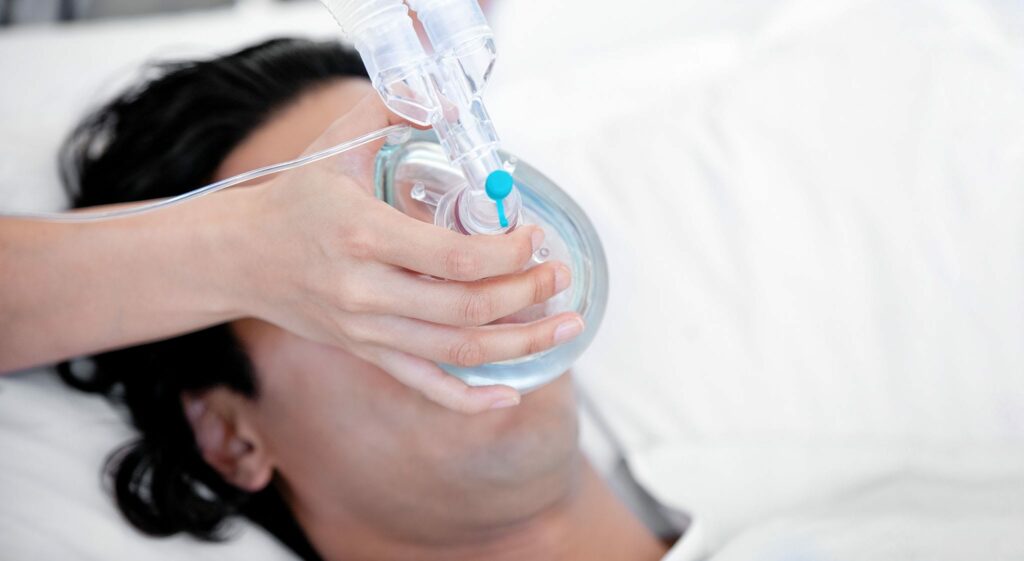
General anaesthesia is the „strongest“ type of anaesthesia. During general anaesthesia, the patient is placed in a deep sleep in which they do not feel any pain, or other feelings, at all and after which they do not remember the procedure. General anaesthesia can be performed intravenously (by catheter injection) or by inhalation (inhalation of gas with a mask).
General anaesthesia is used in cases of complex dental treatment, where the operation takes a long time, requires a lot of surgical manipulations when the operation is performed in different areas of the mouth (e.g. removal of several wisdom teeth), or the patient is psycho-emotionally unstable and sedation is not enough to help relieve the state.
In what cases is the patient offered anaesthesia?
Anaesthesia is offered before any dental procedure during which pain may be felt. The use of anaesthesia is essential for complex surgeries but can be used even during therapeutic procedures. For example, if a patient has hypersensitivity to the gums, anaesthesia can be performed even for professional oral hygiene. In general, the use of anaesthesia depends on the complexity of the procedure, the patient’s endurance, psycho-emotional state, and individual physiological factors.
Is anaesthesia safe?
To ensure patient safety, an experienced anaesthesiologist-resuscitator is involved during sedation and general anaesthesia. While there is always a minimal risk with any type of anaesthesia, the involvement of a qualified anaesthetist, the use of modern safety equipment, ensuring the patient’s general health, and the absence of contraindications before the procedure help to eliminate almost all the possibility of complication. It is important to note that general anaesthesia is only offered in cases of complex dental pathologies, not treating which poses an incomparably higher risk to the general health of the patient.
When is anaesthesia not possible?
There are certain contraindications to performing anaesthesia, the main ones are:
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Exacerbation of acute or chronic diseases (upper respiratory tract disease, asthma, etc.).
- Severe cardiac pathologies (e.g. post-infarction).
- Allergy to certain anaesthetics.
- Major hormonal disorders.
- A full stomach (when the patient eats before anaesthesia).
After anaesthesia
Immediately after local anaesthesia, the area around the injection site should be numb for some time. This sensation completely disappears after about 1 hour.
During sedation, the sleep is shallow, making the patient wake up almost as soon as the anaesthesiologist stops the injection of medication. After general anaesthesia, the patient wakes up quickly (after 15–20 minutes), but a certain postoperative rehabilitation period is required, during which the patient is allowed to rest. After sedation and general anaesthesia, it is recommended that you:
- Do not eat for 1 to 2 hours or while you feel nauseous.
- Do not drive a car for at least 24 hours, as reaction times become slower.
- Do not plan any important, concentration-intensive work or make difficult decisions.
Frequently asked questions
Pricelist
Treatment with local anaesthesia
Adults
| Local anaesthesia | 15 € |
Children
| Local anaesthesia | 15 € |
| Milk tooth dental filling with local anaesthesia | 95 € |
| Treatment of milk tooth pulpitis with local anaesthesia | 120-140 € |
Treatment with sedation
Children
| Sedation | 45 € |
| Milk tooth dental filling with sedation | 150-180 € |
| Treatment of milk tooth pulpitis with sedation | 125-180 € |
Treatment with general anaesthesia
Adults
| Treatment and filling of a single root canal | 200 € |
| Permanent tooth extraction with general anaesthesia | 150-180 € |
| Complex permanent tooth extraction with general anaesthesia | 180-240 € |
Children
| Milk tooth extraction with general anaesthesia | 80 € |
| Milk tooth dental filling with general anaesthesia | 120 € |
| Treatment of milk tooth pulpitis with general anaesthesia | 175 € |
| Treatment of a milk tooth and covering with a standard crown with general anaesthesia | 245 € |
| Permanent tooth dental filling with general anaesthesia | 150 € |
Anaesthesiology services
| First general anaesthesia hour | 350 € |
| Second and subsequent hours of general anaesthesia (price per hour) | 115 € |
| Mask anaesthesia | 180 € |
